Cylinder Calculator 3D
Cylinder graphic:
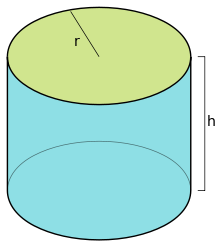
Results:
Insert two values for the cylinder:
Use keys ↑ and ↓ for value changes
r h d = 2·r p = 2·π·r AB = π·r2 AL = 2·π·r·h AS = 2·π·r·(r+h) V = π·r2·hPrecision with 3 decimal places
Interactive 3D-Cylinder
All formulas for the Cylinder at a glance
Here you see the necessary formulas for the calculation of a right circular cylinder:
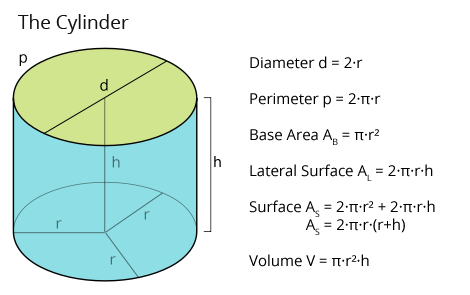
Link to graphic: https://www.matheretter.de/img/wiki/cylinder-formulas.png
Explanations:
Diameter = 2·radius → d = 2·r
Perimeter = 2·Pi·radius → p = 2·π·r
Base Area = Pi·radius² → AB = π·r²
Lateral Surface = perimeter · height → AL = 2·π·r·h
Surface Area = 2·base area + lateral surface → AS = 2·π·r² + 2·π·r·h = 2·π·r·(r+h)
Volume = base area · height → V = π·r²·h
What is a cylinder?
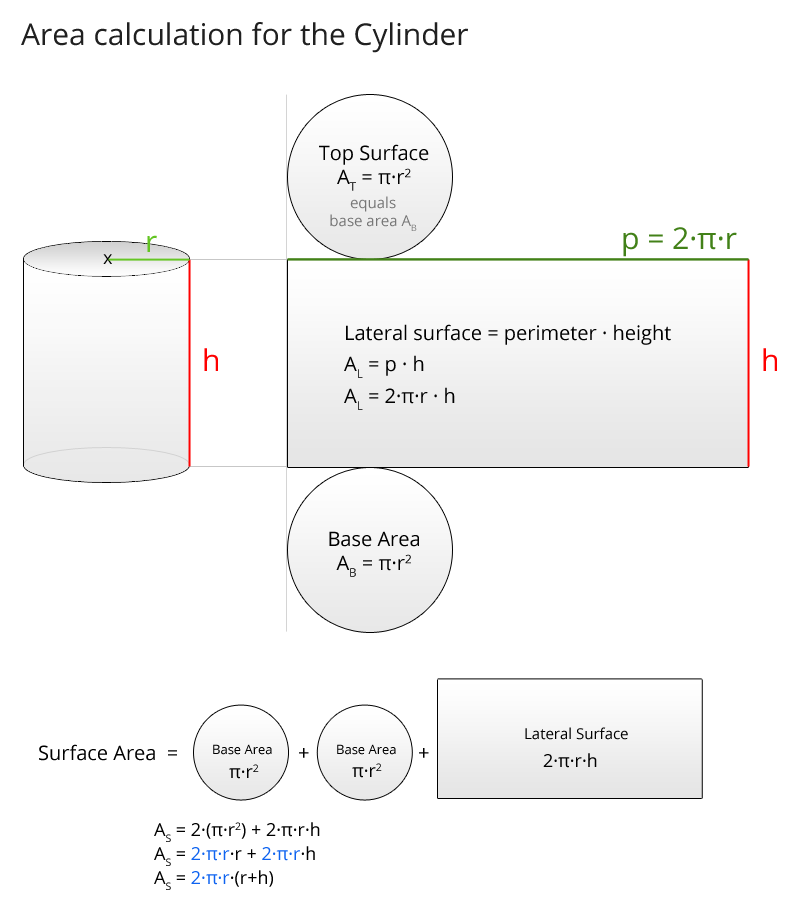
For the circular cylinder there are the following formulas: The perimeter p is 2·Pi·r (this is the formula for the perimeter of the circle), the base area AB is Pi·r² (this is the formula for the area of a circle), the lateral surface is perimeter times height, AL = p·h and therefore AL = 2·Pi·r·h, the surface area consists of the circular areas on top and on bottom (2 times the base area) and the lateral surface, so surface is AS = 2·AB + AL and thus AS = 2·(π·r²) + (2·π·r·h), while the 2·π·r is often factored out and we get: AS = 2·π·r·(r+h). The volume of the cylinder is base area times height, thus V = AB·h = π·r²·h. cylinder with radius, base area and diameter of the base area. Characteristics of a cylinder.
Example from daily life (form of a cylinder):
Drinking glass, pipe, building stone, engine cylinder, chair leg, pen, form of a pill etc.
Flächenberechnung beim Zylinder (Grafik):
Frequently asked Questions about cylinders:
- Calculate the cylinder radius at a given height and surface
- Calculate surface of a cylinder? Exercise
- Cylinder with an attached cone. Calculate the height of the cylinder.
- Calculate volume of a cylinder from only diameter and height
- Complete the following table for cylinders.
- more questions on cylinders...
| Value 1 | Value 2 | Radius computable |
Height computable |
Solution formula for radius Radius is always computable |
Solution formula for height Radius is partially assumed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radius | Height | yes | yes | Radius provided | Height provided |
| Radius | Perimeter | yes | no | Radius provided | Height not computable - Details |
| Radius | Base area | yes | no | Radius provided | Height not computable - Details |
| Radius | Surface area | yes | yes | Radius provided | h = AS / 2·π·r – r See equivalent transformation |
| Radius | Lateral surface | yes | yes | Radius provided | h = AL/2·π·r See equivalent transformation |
| Radius | Volume | yes | yes | Radius provided | h = V/r2·h See equivalent transformation |
| Height | Perimeter | yes | yes | r = p / 2·π See equivalent transformation |
Height provided |
| Height | Base area | yes | yes | r = AB/π See equivalent transformation |
Height provided |
| Height | Surface area | yes | yes | r1,2 = – h/2 ± √( h2/4 + AS/2·π ) See equivalent transformation |
Height provided |
| Height | Lateral surface | yes | yes | r = AL/2·π·h See equivalent transformation |
Height provided |
| Height | Volume | yes | yes | r = ± √( V/h·π ) See equivalent transformation |
Height provided |
| Perimeter | Base area | yes | no | r = p / 2·π See equivalent transformation |
Height not computable - Details |
| Perimeter | Surface area | yes | yes | r = p / 2·π See equivalent transformation |
h = AS / p – r See equivalent transformation |
| Perimeter | Lateral surface | yes | yes | r = p / 2·π See equivalent transformation |
h = AL / p See equivalent transformation |
| Perimeter | Volume | yes | yes | r = p / 2·π See equivalent transformation |
h = 2·V / u·r See equivalent transformation |
| Base area | Surface area | yes | yes | r = AB/π See equivalent transformation |
h = r · AS / 2·AB – r See equivalent transformation |
| Base area | Lateral surface | yes | yes | r = AB/π See equivalent transformation |
h = r · AL / 2·AB See equivalent transformation |
| Base area | Volume | yes | yes | r = AB/π See equivalent transformation |
h = AL / AB See equivalent transformation |
| Surface area | Lateral surface | yes | yes | If we have the height, we can calculate the radius from the formule of the lateral surface: r = AL / 2·π·h See equivalent transformation |
h = ± √( AL2 / 2·π·AS – 2·π·M ) See equivalent transformation |
| Surface area | Volume | yes | yes | 0 = r3 + AS / -2·π · r + V / π 3 Solutions for the cubic equation See equivalent transformation |
If we have the height, we can calculate the radius from the formule of the lateral surface: h = AS / 2·π·r – r See equivalent transformation |
| Lateral surface | Volume | yes | yes | r = 2·V/AL See equivalent transformation |
If we have the height, we can calculate the radius from the formule of the lateral surface: h = AL/2·π·r See equivalent transformation |
